Introduction
I have been seeing a behaviour in some apps for a while, and I’ve always wanted to know how it was done. I noticed some apps that allow to view urls within the app, used something that is “Powered by Chrome”. I first noticed this on the Twitter for Android app, then on Medium, then Feedly.
I was interested in knowing how these worked, but I didn’t know what to search for. Finally, a few weeks ago, I stumbled on “Chrome Custom Tabs”. Alas, that was what I was looking for.
In this post, I’m going to explain why, when and how to use “Chrome Custom Tabs” in your Android applications.
Why use Chrome Custom tabs?
When building apps, developers are usually faced with difficult tradeoffs to make when we have to show web content in our Android apps. Very common and easy solution is to open links externally. If you do this, then these lines of code will look familiar:
Intent browserIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, Uri.parse(url));
startActivity(browserIntent);
This typically results in a heavy-weight transition between the app and web. Launching a browser from your app to view web content results in a huge context switch which isn’t customizable, and hence could lead to a terrible experience.
An improvement on this experience will be to use a WebView which is essentially an Android view that displays web pages. However, this options requires technical work to implement and delivers a browsing experience that the users aren’t used to.
To solve this problem, the Google Chrome team introduced a new feature last September, called custom tabs. This allows to load a chrome tab within your app, and also allows you customize the look and feel of Chrome thereby making the transition between your app and the web content fast & seamless for your users.
This is Chrome Custom tab in action on Twitter for Android app:

Chrome Custom tab allows you customize the experience of Chrome. It allows you customize:
- Toolbar color
- Enter and exit animations
- Add custom actions to the Chrome toolbar, overflow menu and bottom toolbar
How to use Chrome Custom tabs
1. Add Chrome Custom tabs to your app
First thing to do, is to add the chrome custom tabs dependency to the dependencies section of your
app-level build.gradle file. The section should look like this
dependencies {
...
compile 'com.android.support:customtabs:23.4.0'
}
With this, you can customize the look and feel of Chrome, and also take advantage of some optimizations, as we will see later in the post.
2. Open a Chrome custom tab
Next step is to proceed to open a Chrome custom tab. In this step, you get to configure the look and feel of Chrome open a url in the Chrome Custom Tab. This happens in 3 easy steps:
- Create a CustomTabsIntent builder for customization. Specify all the custom properties you desire.
- Build a CustomTabsIntent from the builder
- Launch the url.
This block of code, does exactly the 3 things listed above:
...
Uri uri = Uri.parse("https://segunfamisa.com");
// create an intent builder
CustomTabsIntent.Builder intentBuilder = new CustomTabsIntent.Builder();
// Begin customizing
// set toolbar colors
intentBuilder.setToolbarColor(ContextCompat.getColor(this, R.color.colorPrimary));
intentBuilder.setSecondaryToolbarColor(ContextCompat.getColor(this, R.color.colorPrimaryDark));
// set start and exit animations
intentBuilder.setStartAnimations(this, R.anim.slide_in_right, R.anim.slide_out_left);
intentBuilder.setExitAnimations(this, android.R.anim.slide_in_left,
android.R.anim.slide_out_right);
// build custom tabs intent
CustomTabsIntent customTabsIntent = intentBuilder.build();
// launch the url
customTabsIntent.launchUrl(activity, uri);
3. Further customization
a. Setting an Action Button
You can set an action button and customize that action button.
// Add an Action Button to the Toolbar.
// 'icon' is a Bitmap to be used as the image source for the
// action button.
// 'description' is a String be used as an accessible description for the button.
// 'pendingIntent is a PendingIntent to launch when the action button
// or menu item was tapped. Chrome will be calling PendingIntent#send() on
// taps after adding the url as data. The client app can call
// Intent#getDataString() to get the url.
// 'tint' is a boolean that defines if the Action Button should be tinted.
builder.setActionButton(icon, description, pendingIntent, tint);
An action button is what is highlighted by the red box in the image below:
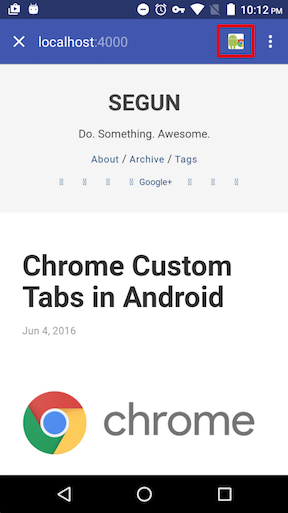
b. Adding custom menu items.
You can also add custom menu items. To do this, follow these steps:
// Add menu item to the Chrome tab menu
// 'label' is the label to show in the menu item
// 'pendingIntent' is is a PendingIntent to launch when the action button
// or menu item was tapped. Chrome will be calling PendingIntent#send() on
// taps after adding the url as data. The client app can call
// Intent#getDataString() to get the url.
intentBuilder.addMenuItem(label, pendingIntent);
Custom menu items added are as highlighted in the image below:

c. Adding entry and exit animations.
It’s also possible to specify custom entry and exit animations. To do this, follow these steps:
// set start animation
// chrome slides in from the right, and host activity slides out from the left.
intentBuilder.setStartAnimations(this, R.anim.slide_in_right, R.anim.slide_out_left);
// set exit animation.
// host activity slides in from the left and chrome slides out from the right.
intentBuilder.setExitAnimations(this, android.R.anim.slide_in_left,
android.R.anim.slide_out_right);
Advanced customization of Chrome custom tabs
There are other advanced customizations you can do, especially when it comes to optimization. Chrome Custom Tabs allows for:
- Warming up Chrome to make pages load faster,
- Tell Chrome what the user is likely to open, and then allow for prefetching the content,
- Create a new tab session,
- Connection to the Chrome service,
- Custom Tabs connection callbacks,
- Create fallbacks when there is no version of Chrome that supports Chrome Custom Tabs, or where there isn’t chrome at all.
Want to see more code?
Clone or download this github repo for the full source code to demo Chrome Custom Tabs.
The repository contains code to customize the tabs, helper methods, more code on the optimization, warming, binding to a Chrome Tab Connection, Unbinding at the right time, fallback method, for when the device doesn’t have Chrome installed.
References and Further reading
This post is just an introduction to using Chrome Custom Tabs, feel free to explore more resources to gain a deeper insight into using Chrome custom tabs.
Here are some references and resources for further reading:
- http://android-developers.blogspot.com.ng/2015/09/chrome-custom-tabs-smooth-transition.html
- https://github.com/GoogleChrome/custom-tabs-client/blob/master/Using.md
- https://github.com/GoogleChrome/custom-tabs-client
- https://developer.chrome.com/multidevice/android/customtabs
If you have any comments/suggestions or corrections, I’d love to hear them. Please do not hesitate to drop a comment below or tweet at me.
Please share if this post has helped you in some way, or you know someone it may be of help to. 🙈😁
Cheers :)